Kidney disease is one of the most underestimated health conditions in the world—not because it’s rare, but because it hides so well. Millions of people live with early kidney disease without knowing it, often until serious damage has already occurred.
The reason is simple: early signs of kidney disease are subtle, painless, and easy to dismiss. Fatigue feels normal. Swelling seems temporary. Changes in urination are ignored. Yet these quiet signals are the body’s early warning system.
At Pulse Multispeciality Hospital, doctors frequently see patients who wish they had recognized these signs earlier—when treatment options were simpler and outcomes far better.
Why Kidney Disease Is Often Diagnosed Too Late
The kidneys are extraordinary organs. They continue working even when significantly
damaged, masking symptoms until
function drops dangerously low.
Key reasons kidney disease goes unnoticed:
- The body compensates for declining kidney function
- Symptoms develop slowly over months or years
- Early signs mimic common lifestyle issues
- There is little or no pain in early stages
What Do the Kidneys Do—and Why It Matters
Your kidneys are not just “urine-producing organs.” They are central to overall health.
Healthy kidneys:
- Filter waste and toxins from blood
- Regulate fluid and electrolyte balance
- Control blood pressure
- Produce hormones for red blood cell formation
- Maintain bone strength through vitamin D regulation
When kidneys begin to fail, multiple systems are affected simultaneously, which explains the wide range of early symptoms.
What Is Kidney Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
Kidney disease refers to any condition that reduces the kidneys’ ability to function
properly. When this damage
lasts longer than three months, it is classified as chronic kidney disease (CKD).
CKD Stages (Patient-Friendly Overview):
- Stage 1: Kidney damage with normal function; no symptoms
- Stage 2:Mild loss of function; subtle signs begin
- Stage 3:Moderate damage; symptoms become noticeable
- Stage 4: Severe loss; serious complications
- Stage 5:Kidney failure; dialysis or transplant required
Why Early Detection of Kidney Disease Changes Everything
Kidney disease affects far more than the kidneys. It significantly increases the risk of
:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Anemia
- Bone weakness
- Fluid overload and lung complications
Early diagnosis allows timely intervention. Specialists at Pulse Multispeciality Hospital emphasize that patients diagnosed early often avoid dialysis and maintain a good quality of life for many years.
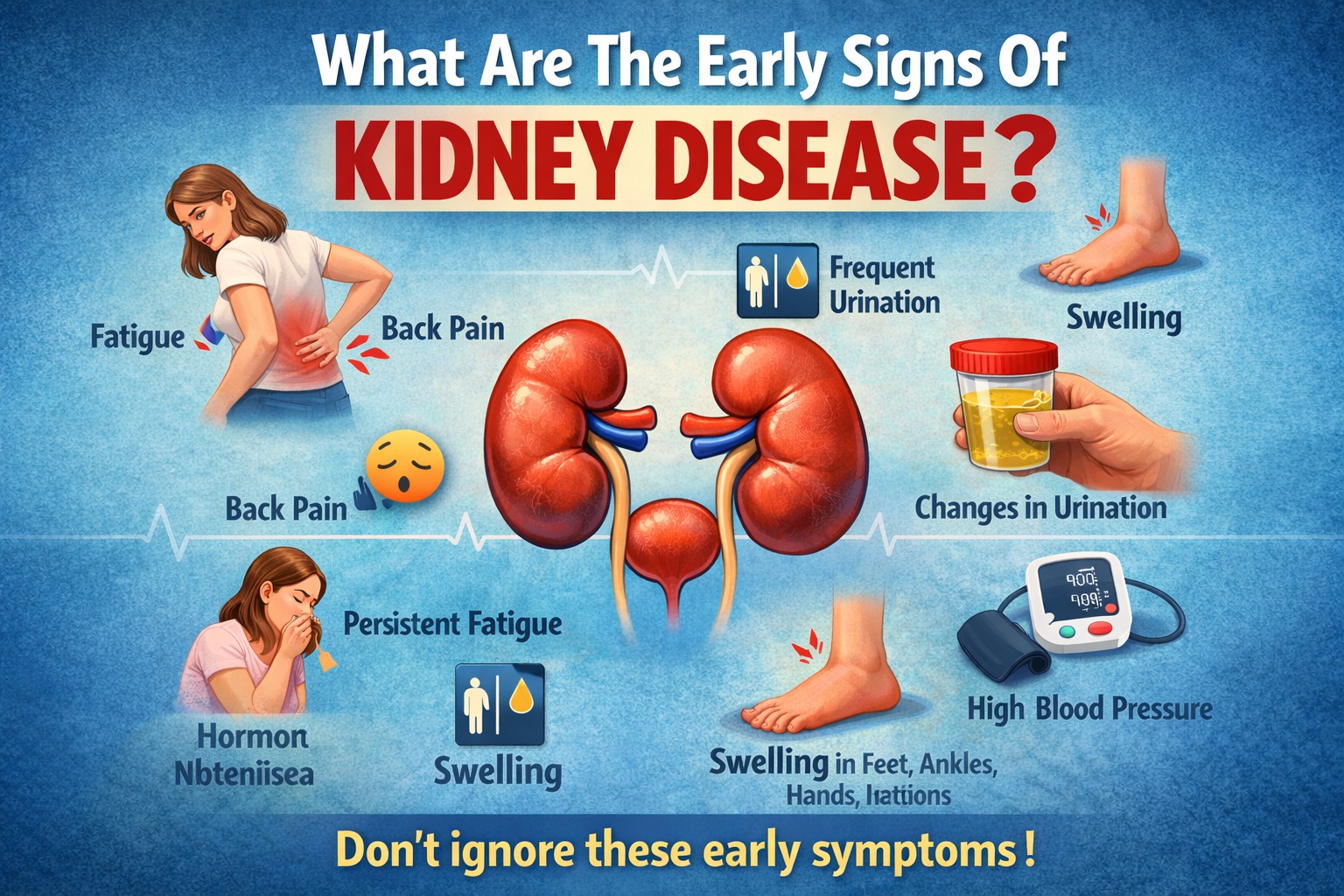
What Are the Early Signs of Kidney Disease?
1. Changes in Urination
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Reduced urine output
- Dark, cloudy, or tea-colored urine
- Foamy or bubbly urine
- Blood in the urine
Foamy urine is an especially important early warning sign, often linked to protein leakage.
2. Swelling (Edema) in Feet, Ankles, Hands, or Face
- Swollen feet or ankles by evening
- Puffiness around the eyes in the morning
- Tight rings or shoes
This happens when kidneys can’t remove excess salt and fluid effectively.
3. Persistent Fatigue and Low Energy
- Constant tiredness
- Weakness
- Reduced stamina
This fatigue often feels deeper than everyday tiredness.
4. Appetite Loss, Nausea, and Digestive Issues
- Reduced appetite
- Nausea or vomiting
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Unintentional weight loss
These symptoms are often mistaken for stomach or liver problems.
Skin and Mouth Changes
- Dry, itchy skin
- Pale or darkened skin tone
- Ammonia-like breath or mouth ulcers
These signs result from toxin buildup in the blood.
6. Brain Fog and Poor Concentration
- Focus declines
- Memory weakens
- Mental clarity reduces
This is frequently overlooked or blamed on stress.
7. Muscle Cramps and Sleep Problems
- Night-time muscle cramps
- Restless sleep
- Insomnia
Early Kidney Disease Symptoms in Men and Women
In men: erectile dysfunction, reduced libido, urinary flow changesIn women: frequent urinary infections, hormonal imbalance, swelling during pregnancy
Who Is at Higher Risk?
The best way to fight heart disease is to prevent it. Here’s how:
- Diabetes or prediabetes
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Family history of kidney disease
- Obesity or smoking habits
- Long-term painkiller use
high-risk individuals even if no symptoms are present.
How Is Kidney Disease Detected Early?
Early kidney disease is detected through:
- Blood tests (Creatinine, eGFR)
- Urine tests (Albumin, protein levels)
- Blood pressure monitoring
- Imaging tests when required
When Should You See a Doctor?
Do not delay medical evaluation if you notice:
- Persistent swelling
- Foamy or bloody urine
- Severe or worsening fatigue
- Appetite loss lasting several weeks
Early medical advice can prevent permanent kidney damage.
Early Awareness Protects Your Kidneys
Kidney disease begins quietly, but its consequences are serious. Recognizing the early signs of kidney disease gives you the chance to act early, protect kidney function, and maintain long-term health.
Listening to your body and seeking timely care especially from a trusted Nephrology Hospital in Tathawade PCMC can make all the difference in preventing complications and preserving kidney health.